
What are the biggest obstacles in the growth of SMEs?
Given the huge importance of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises to social, economic and environmental development, the future of work will be desolate if we do not support SMEs to unlock their full potential. SMEs account for 90% of businesses and employing about 50% of the workforce across the world. In emerging economies, SMEs contribute up to 40% of GDP, according to the World Bank. However, their relatively small size makes them vulnerable to external shocks.
In this article, we have listed down 5 major challenges in the growth of SMEs.
1. Funding or Financing Gap
The lack of funding and finance is one of the major factors that hinder SMEs to grow, fully exploiting profitable investment opportunities. As estimated by the International Finance Corporation, 65 million firms, or 40% of formal micro, small and medium enterprises (MSMEs) in developing countries, have an unfulfilled financing need of $5.2 trillion every year, which is equivalent to 1.4 times the current level of the global MSME lending. Mainstream lenders are often unwilling and dubious to invest in SMEs are considering it as less attractive investment opportunities, given the high levels of uncertainty and risk involved. There is a competitive market for the limited supply of investors’ funds and larger companies having a huge appetite for the funds available, the SMEs are often left out.
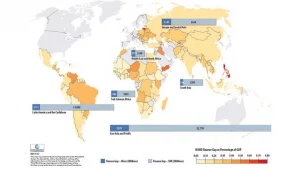
Source: The World Bank
2. Lack of Marketing Competence
As per the survey conducted on 1,000 small business owners by Campaign Monitor, 20.8% have at least one employee who does marketing in addition to other tasks, while 15.3% say the owner executes all of their marketing. A few marketing concerns that are frequently vocalized are lack of resources, increasing visibility, generating quality leads, execution of effective marketing activities and keeping up with trends and technology. SMEs need to get smart about how they market effectively, given the common limitations that nearly all small businesses undergo.
3. Digital and Technological Gap
Digitization and technology are developing rapidly. The use of smartphones and tablet computers has also grown over the years. In accordance with that, more consumers now prefer Internet sales to manual sales and the e-commerce market for individuals has expanded too. However, still, a significant number of SMEs have been unable to sufficiently utilize such opportunities. According to Digital Economy and Society Index (DESI) 2020 data, while businesses are getting more and more digitized, only a fraction of SMEs rely on advanced cloud (17%) and big data applications (12%), despite being connected to the internet at the same rate. SMEs need to rethink and redesign their businesses, focusing on how to leverage web, social media, mobile connectivity, data analytics and incorporate these tools in their business model.
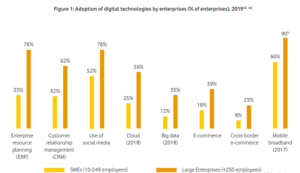
Source: Vodafone Group
4. Lack of Skilled WorkForce
Large enterprises can always invest more in training and equipment. They pay a higher salary, offering better working conditions to the workers. SMEs fail when it comes to productivity and quality employment. In developing countries, this gap leads to low-income generation and substandard growth performance. Due to the lack of resources and knowledge, SMEs are hesitant to invest in a skilled workforce. If we see it from the workers’ point of view, the wages provided by SMEs are 20% – 30% lower than the national average and the gender gap between male and female-owned SMEs still persists. To increase profits, productivity and quality employment, SMEs can try to incorporate the Value Chain business model. It will allow them to provide better jobs and in turn, ensure sustainable growth and benefits for the workers.
5.Government Regulations
The government’s collar around owners’ necks seems to become tighter every year. Every Micro, Small or Medium enterprise has to comply with multiple regulations which include taxes, environmental and certain sector-specific regulatory laws and licenses. Every enterprise has to undergo several clearances. For e.g. a dairy or a food production unit would require clearance from Agriculture and Food Processing Industries Department and someone in electrical appliance production would have to get authorization from the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS).
Mostly, the employees working in SMEs get updated about the changes in the law through their peers in the industry or newspapers and other media sources. There is no structured process for the flow of updates to the SMEs. All the information they get is through unofficial resources and often delayed.
Conclusion
These challenges might change over time, but will never actually go away. As a business owner, you need to develop a plan to meet these challenges head-on and manage them effectively. Let us know if you’re facing any other challenges besides the ones mentioned above.
+ There are no comments
Add yours